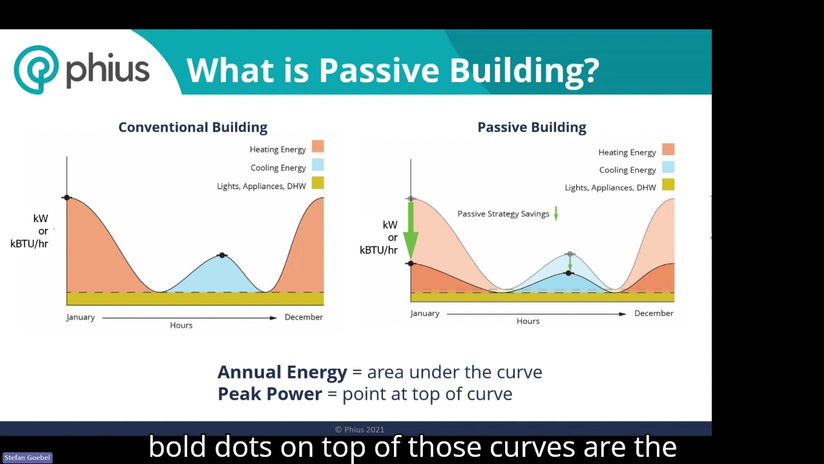
Passive House & Net Zero Energy Buildings
Passive buildings, often referred to as passive house (from the German "Passivhaus"), are highly energy-efficient buildings designed to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures year-round with minimal energy use. They achieve this by optimizing their design, insulation, and air tightness, reducing the need for conventional heating or cooling systems. The key principles include:
1. Continuous Insulation (incl. roofs, walls and floors) to minimize heat loss or gain (helps keep indoor temperatures stable) and avoid thermal bridging (enhancing building durability and avoiding mold growth).
2. Shading and High Performance Windows/Facades to properly balance heat gain and heat loss.
3. Airtight Construction to reduce keeping the building envelope sealed to prevent drafts and air leaks, reducing energy loss and enhancing building durability.
4. Energy / Heat recovery ventilation to provide fresh air to occupants 24/7. It reclaims heat from the exhaust air on it’s way out and uses that heat to pre-treat incoming, fresh air. Enthalpy (or Energy) recovery ventilation (ERV) regulates humidity in addition to heat, HRV’s do not. By using an HRV or ERV, less energy is needed to heat or cool interior spaces.
By following these principles, passive buildings can reduce energy consumption by up to 90% compared to conventional buildings, making them extremely eco-friendly and cost-effective in the long run.